
Why Are Baby Teeth Important?
There are many misconceptions about primary or baby teeth. Parents are often unaware that baby teeth are critically important to their children’s oral health, their ability to enjoy a healthy diet, speak well, and especially to their self-esteem. When a young child’s teeth look like the “before” shots in this post, they may not be able to articulate that they are in pain or being bullied or outcast by other children for their appearance. Primary teeth can end up looking like this due to various conditions including advanced decay, discoloration resulting from decay or medications, and infections.
Cavities in baby teeth
Tooth decay is one of the most common and preventable childhood diseases in the United States and is even more common than obesity and asthma. Untreated, cavities in baby teeth can cause pain and infections that can lead to difficulty eating, talking, playing, sleeping, and learning. Kids with severe cavities usually miss more school than those with good oral health. Another potentially serious consequence of untreated dental disease is being more vulnerable to infections in other areas of the body, such as in the ears and sinuses.
More than 50% of children 6 to 8 years of age have experienced at least one cavity in their baby teeth. One in five children have had a cavity by kindergarten age and more than 50% have had cavities by the time they reach 8 years old. Their risk is higher if their community water is not fluoridated, they are not brushing with fluoride toothpaste, have not been treated with fluoride varnish, and do not have a dental home. Parents and siblings with a propensity for cavities and poor diet can also influence risk.
Benefits of pediatric crowns vs fillings
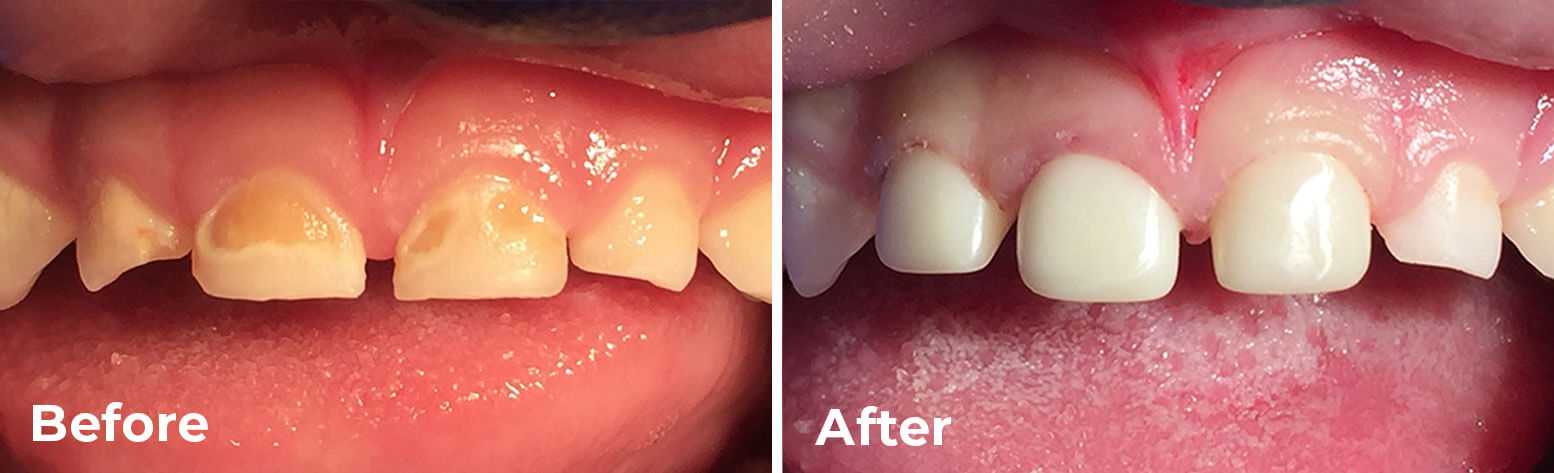
If the extent of a child’s carious lesions is too great to support large amalgam or tooth-colored restorations, the best choice for them may be a pediatric zirconia crown. Large fillings in baby teeth are subject to fracture, which leads to cracked teeth, re-treatment, and sometimes the necessity for a root canal, often a costly inconvenience that may still result in pain and additional future failure.
Zirconia crowns, as well as stainless-steel crowns, ensure proper function and protect baby teeth from further decay. Tooth-colored zirconia crowns can be placed on either front or back teeth and will improve a child’s appearance, especially in anterior teeth.
Other positive attributes of pediatric crowns versus fillings are that crowns cover most of the tooth, protecting it from further decay, which is important for children with a high caries risk. They also prolong the life of the primary tooth, which is necessary to ensure the proper space between the baby teeth is maintained for erupting adult teeth to fit into.
Undergoing multiple restorations in a baby tooth can cause a lot of stress and discomfort for young children. Tooth preparation for a pediatric crown may take a little longer than placing a filling, but most children can be fitted with a crown at the same appointment, minimizing trauma and time spent in the dental office.
Why zirconia crowns for baby teeth
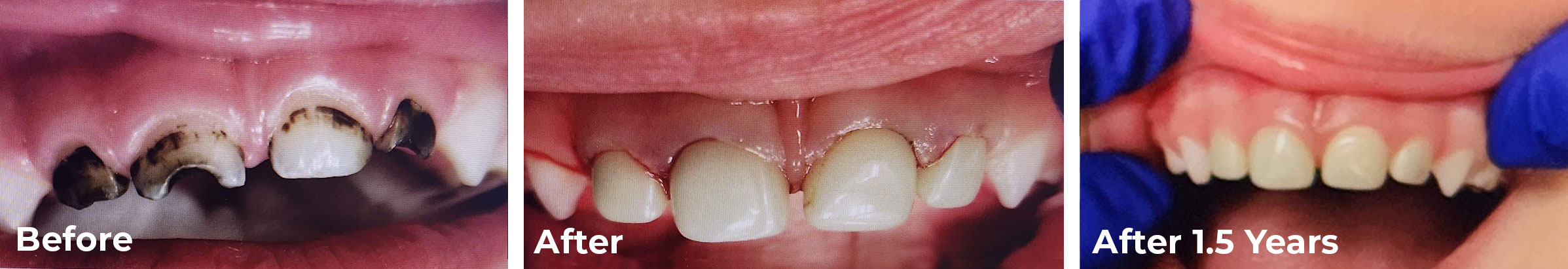
Zirconia is available in different formulations. Monolithic zirconia, the type Cheng Crowns utilizes, is incredibly durable and reflects light like natural teeth do, so it will blend well with surrounding teeth. A monolithic zirconia crown provides strength to the underlying tooth that aids in proper chewing and developing speech and fits snugly to protect a child’s tooth from future decay. Finally, in case you were wondering, a zirconia crown will last until the baby tooth naturally falls out like other baby teeth—so don’t worry about disappointing the tooth fairy.
Conclusion
Baby teeth play a vital role in a child’s overall well-being, far beyond just their appearance. They have a profound impact on a child’s oral health, dietary habits, ability to speak, and self-esteem. The prevalence of cavities in baby teeth is a concern, with significant consequences if left untreated, including pain, infections, and missed school days. Fortunately, the choice between pediatric crowns and fillings offers a promising solution, with zirconia crowns standing out as a durable and aesthetically pleasing option.
By understanding the importance of baby teeth and taking proactive steps to maintain their health, parents can ensure their children’s well-being and lay the foundation for a lifetime of healthy smiles. Caring for baby teeth is not just a matter of aesthetics but a critical aspect of a child’s overall development and happiness.
Resources
Casamassimo PS, Chin JR, Conte CE, et al. Treating Tooth Decay: How to Make the Best Restorative Choices for Children’s Health. Chicago, IL: Pediatric Oral Health Research and Policy Center, American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry; 2020.
Children’s Oral Health. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Available at https://www.cdc.gov/oralhealth/basics/childrens-oral-health/index.html. Accessed January 16, 2023.
Do Baby Teeth With Crowns Fall Out On Their Own? Warr Pediatric Dental Associates. Available at https://warrpda.org/do-baby-teeth-crowns-fall-out/?utm_source=rss&utm_medium=rss&utm_campaign=do-baby-teeth-crowns-fall-out#:~:text=Yes%2C%20baby%20teeth%20with%20crowns,to%20keep%20it%20or%20not. Accessed January 16, 2023.
Children’s Oral Health. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Available at https://www.cdc.gov/oralhealth/basics/childrens-oral-health/index.html. Accessed January 16, 2023.
The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ). Available at https://www.aapd.org/resources/parent/faq/. Accessed January